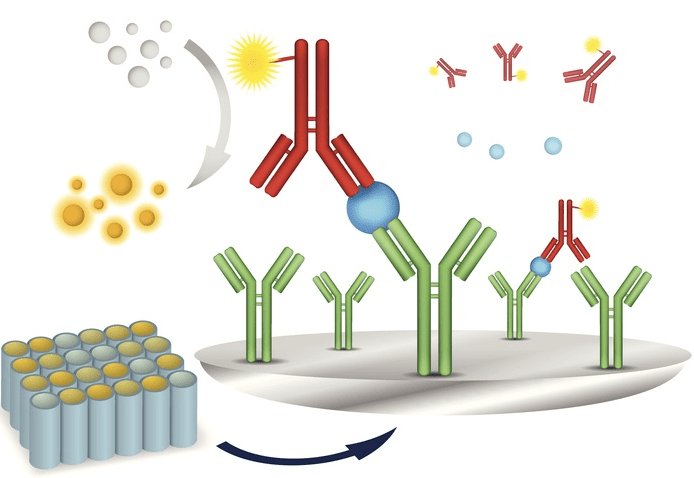
Immunoassays are tests that detect the presence of a specific molecule in a sample using antibody-antigen binding reactions. Antibodies will only bind to the specific structure of a particular antigen and nothing else, making immunoassays highly specific. This makes antibodies effective reagents for detecting target molecules. As a result, immunoassays are a fundamental tool for clinical diagnostics, life science research, and industry laboratories. Different types of immunoassays can come in a range of formats, and can be used to assess varying diseases, track proteins, and detect environmental contamination.
Antibodies are an important part of the immune system. When the body is infected with an antigen the immune system generates white blood cells that release antibodies specific to that antigen. These antibodies detect and bind to antigens, making it easier for white blood cells to target and destroy invading pathogens. The techniques that are routinely used in biotechnology capitalizes upon this natural immune process. Antibodies are used in many research applications as well as in immunoassays for disease detection. For example, the specificity of antigen-antibody binding is used in immunoprecipitation and ELISA assays, and fluorophore-conjugated or enzyme-tagged antibodies can be used for labeling molecular targets on individual cells and whole tissue. Antibody purification techniques can also be used to develop biosensors to facilitate disease detection.
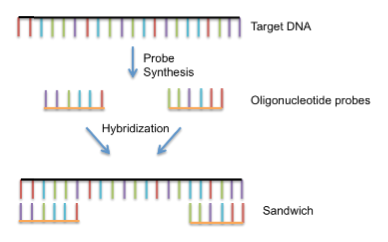
Sandwich DNA/RNA hybridization is a technique designed for the detection and quantitation of nucleic acids within crude biological samples. DNA/RNA sandwich hybridization has also widely been used not only to identify a specific DNA/RNA sequence, but also to distinguish single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between wild-type and mutant DNA/RNA.

Immunoprecipitation (IP) is a technique for capturing specific proteins from a complex solution via antibody-antigen affinity. In IP the goal is to target and isolate a specific protein, whereas in co-IP the goal is to identify protein complexes and other macromolecules bound to the target in the sample solution. The targeted protein complexes can later undergo analysis to identify specific binding partners, determine binding affinities, or study the kinetic relationship between binding and the function of the target protein. Recently, magnetic nanoparticle technologies have greatly advanced co-IP experiments. Magnetic co-IP protocols offer simple, ultra-fast workflows, versatility, and help generate highly concentrated complexes. After performing a magnetic co-IP protocol, the protein capture efficiency can be measured by IP input, which is essentially the total protein lysate and what is eluted from the magnetic beads after. The IP is often tested through SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis.

Magnetic nanoparticles have risen in popularity in medical and biotechnology fields over the past decade. The ideal magnetic properties of nanoparticles for biomedical applications are that they exhibit a form of magnetism called superparamagnetism, where they can be magnetized by an externally applied magnetic field and quickly returned to a non-magnetic state once the field is removed. This feature also prevents magnetic nanoparticles from exhibiting an active behavior when there is no applied field.
In vitro Diagnostic (IVD) assays are used to diagnose infection or disease by specifically targeting a unique surface antigen or DNA sequence. IVD assays can be used to monitor a person’s overall health or to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases. Magnetic beads have been developed to aid in molecular diagnostics, and provide the great advantage of simple manipulation via a magnet. In nucleic acid detection, magnetic beads act as a capture support for fast, easy, biomolecule separation. The surfaces of magnetic beads can be modified with IVD coatings for differing applications to allow for the specific identification and capture of target microbes. Magnetic IVD coatings can enhance the sensitivity and specificity of detection for the rapid diagnosis of a disease, point of care use, or for the quantitation of a specific microbe in a research setting.
Superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are small synthetic maghemite (γ-Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), hermatite (α-Fe2O3) particles and mixed oxides of iron with transition metal ions (e.g. copper, cobalt, nickel, and manganese) with a core from 10-100 nm in diameter. Magnetite and maghemite nanoparticles are the most widely used SPIONs in various biomedical applications both as diagnostic, therapeutic and imaging purposes.
Cell isolation is a critical step in the biomedical science and research sector and has been employed in in-vitro diagnostic tests and biological samples. The procedure of cell isolation lies on the specificity of a certain antibody toward its antigen. In recent decades magnetic beads have been implemented for the immunomagnetic separation protocols using both the superparamagnetic properties and antibody-antigen specificity which can be tuned to the experimental goal, and can produce high yields and highly enriched targets when used properly. Basically, cells of interest possess unique identifying surface antigens for the targeting beads. The immunomagnetic separation protocol follows these general steps:
Regardless of the introduction of broad-spectrum antibiotics, pathogenic bacteria are still the main cause of life-threatening infectious diseases in the world. Prompt detection of pathogens with the lowest concentrations (<100 cfu/mL) without time-consuming procedures, such as culture or amplification by PCR is very important in disease diagnosis and the subsequent treatment regimen.
Introduction
With the advent of nanomedicine in recent decades numerous nanomaterials have been used for the formulation and synthesis of nanoparticles. A nanoparticle is defined as a tiny particle with a size ranging 1-100 nm. Among the different types of nanomaterials, magnetic gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have attracted much attention in the last decades. The two physical and chemical fundamental properties of GNPs are affected by their nanostructure – shape and crystal texture – which allows them to have numerous biomedical applications in prophylaxis, diagnosis and treatment.

Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) are particles of nanosized range (10−9 nm)(usually ,100 nm in size) with unique properties of magnetic targeting, biocompatibility, surface modification characteristics and superparamagnetic properties. The application of magnetism in medical science was first introduced in the 1950s for “magnetic hyperthermia therapy” (cancer cell death) leading to various MNPs’ syntheses including Superparamagnetic iron oxide NPs (SPIONs).
A fusion protein is a protein composed of several domains (parts) that are encoded by separate genes and have been joined so that they are transcribed and translated as a single unit, producing a single polypeptide maintaining functional properties of each original protein. Fusion proteins can be created “in vivo” and “in vitro” by using recombinant DNA techniques for use in biological research or therapeutics. Fusion proteins occur naturally and commonly in cancer cells, where they may function as oncoproteins having different functions or physico-chemical patterns.
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) are diagnostic tests performed on biological samples (e.g. blood, tissue) obtained from the body to detect DNA/RNA, microorganisms, or biological biomolecules (e.g. protein) associated with diseases, infections or medical conditions. The IVD tests are generally non-invasive, used both in professional healthcare settings and at home as rapid kits and are useful for early detection of diseases, prevent the spread of diseases and improve patient care and management.
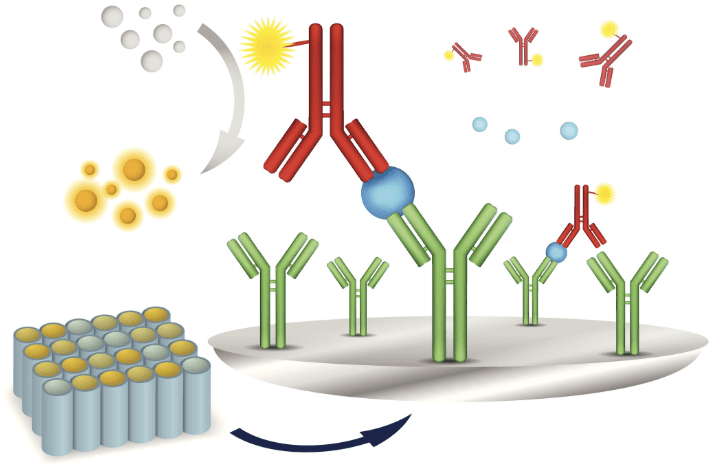
The sandwich ELISA is one of the Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) methods which are analytical techniques for the detection of various compounds/analytes in a sample in the biomedical and research setting.

Isolation and identification of cell(s) is the prerequisite step for many fields of research, such as cell function and analysis, signaling and gene expression. Techniques that enable the rapid and accurate enrichment of target cell populations are therefore an area of substantial interest. The output of cell-sorting techniques from the cell suspension is based on higher efficacy or throughput, purity, and recovery. Based on the different principles used, the Cell sorting techniques are categorized into two general categories:
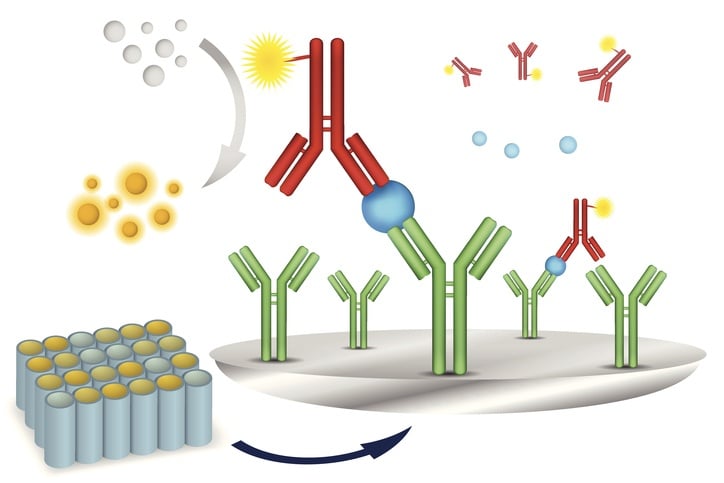
Immunoassay techniques are methods for the sensitive and specific quantitative detection of chemical substances such as hormones, drugs and specific proteins that utilize the highly specific binding between an antigen or hapten and homologous antibodies.
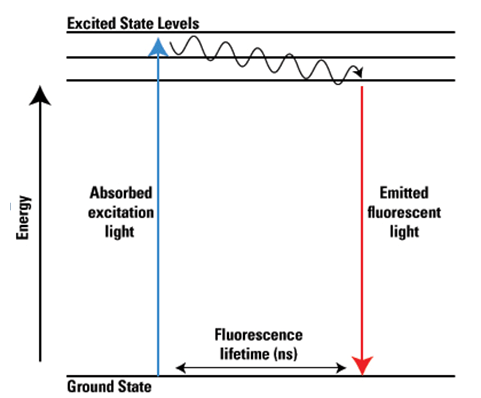
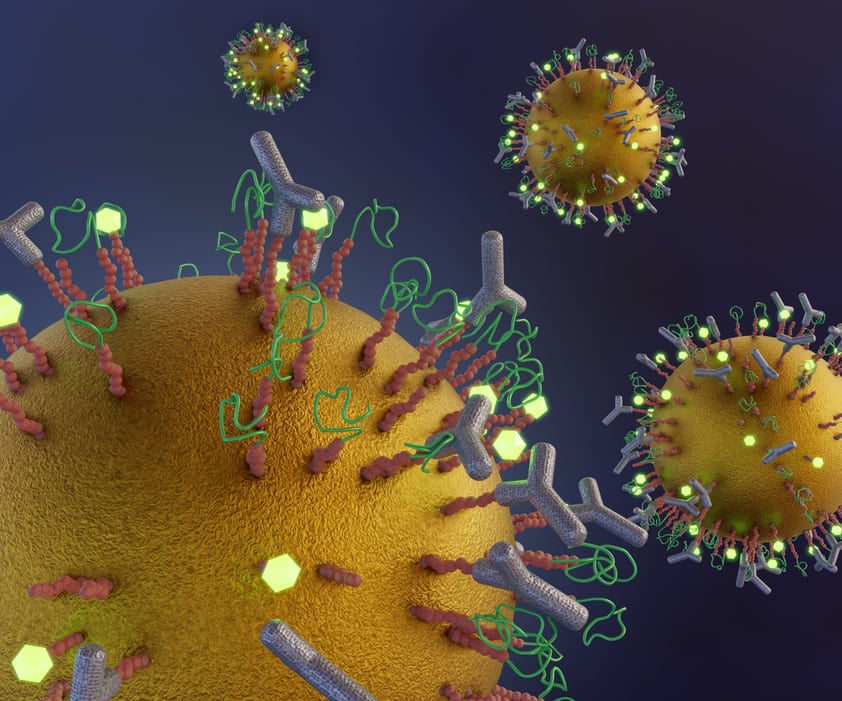
While chemiluminescence and fluorescence are used interchangeably, especially when referring to tracking strategies for magnetic separation in biosensors or in-vitro diagnostic assays, however, they are different concepts. They both give off a photon as an electron relaxes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, but the difference lies in the method used to excite that electron to a higher energy state in the first place. In fluorescence the electron is kicked up to a higher energy state by the addition of a photon. In chemiluminescence the electron is in a high-energy state due to the creation of an unstable intermediate in a chemical reaction. Light is released when the intermediate breaks down into the final products of the reaction.

The separation of charged biomolecules of a solution by their size and molecular weight is common for scientific studies and biomedical techniques for which various techniques of “electrophoresis” use an electric field, protein electrophoresis is among the widely used procedures.
Poly-L-lysine is a synthetic amino acid polymer – a chain ofmultiple L-lysine amino acid monomers, with multiple industry and biomedical applications.
As a monomer, lysine contains two amino groups, called α-polylysine and ε-polylysine, based on which carbon they are on. Α-polylysine is composed of either L-lysine or D-lysine enantiomers, based on the chirality (“handedness”) of the lysine’s central carbon. Poly-L-lysine is a polypeptide formed from L-lysine monomers. Poly-D-lysine, a similar molecule used in similar applications, is a polymer formed with D-lysine units.
Magnetic bead-based fluorescent immunoassays can detect and measure single or multiple analytes, such as certain proteins, present in one sample. The technology uses fluorescent magnetic beads, such as StrepTalontm or Luminex® beads, and detection antibodies to detect multiple analytes, and therefore answer multiple questions, simultaneously. So how do they work?
Transfection is a technique that makes it possible to modify the genetic content and therefore gene expression of host eukaryotic cells, both in vivo and in vitro. This makes transfection an important tool for drug discovery, the CRISPR-Cas9 technique, studying cell biology, cellular functions and molecular mechanisms of disease. The process centers on inserting proteins, nanoparticles or nucleic acids (such as cDNA, mRNA) into the cytoplasm of cells.

Previously, the use of magnetic beads was limited to small volumes. The difficulty of scaling up beyond a few milliliters was misinterpreted as a limitation of the technology itself. However, as discussed in this e-book, the problem is not the biomagnetic separation process, but a lack of understanding of the physical processes governing it. Once you identify the key parameters that control the magnetic bead's behavior, it is easy to choose the right tools and methods to validate the process and replicate it at different volumes.

Once you have defined the required magnetic force, with a constant magnetic force separation device, it is simple to scale up production. Having validated the magnetic force at a small scale, the same force value can be used for a larger system, even in a different magnetic separation system. Because the conditions remain the same, efficiency (no losses) and batch consistency (no irreversible aggregation) are guaranteed.

When designing a magnetic separation strategy, it is easy to get caught up in the properties of the superparamagnetic beads and how to coat them with the biomolecule of interest (antibodies, antigens, DNA, RNA, oligonucleotides, aptamers...). It is exciting to choose a bead and tailor its surface ligands to perfectly match your target molecule, but don’t stop there! The magnetic separation rack is equally important to a successful identification, isolation, or enrichment protocol. After all, a perfectly designed bead will be useless without a properly designed magnetic rack to efficiently recover it from the solution.
In the recent decades, proteins gained importance after the advent of more advanced analytical procedures and novel genetic or molecular engineering methods. Proteins are cell products and have various physiological functions in the body. Hence, any abnormality in gene expression (mRNA defects), amino acid sequence or structural dysfunction of proteins leads to severe diseases and pathological conditions.

Under constant magnetic force conditions, optical monitoring of the biomagnetic separation process provides information on both when the separation is complete and the characteristics of the magnetic bead suspension.

Protein purification is a fundamental part of studying proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids, necessary for a wide range of clinical, research and industry applications. But choosing the most appropriate protein purification system can be challenging, especially for researchers who are just starting to think about automating their protein purification protocols.

Constant magnetic force separation systems generate the same conditions for all magnetic beads in the suspension. As bead behavior is consistent at every point of the working volume, any changes in the suspension's opacity can be directly related to changes in the suspension’s characteristics.

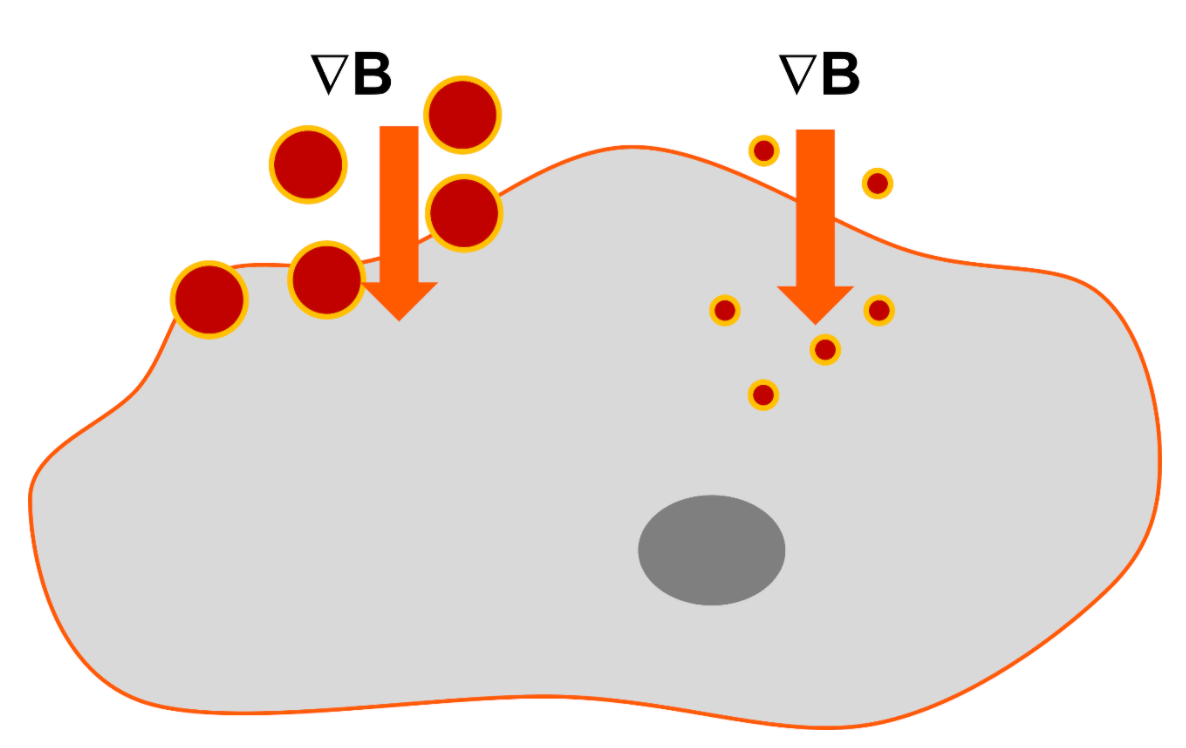
To ensure a consistent biomagnetic separation process, all the magnetic beads should experience the same conditions. Controlling the magnetic force is key to achieving consistency within and between batches, especially when scaling up. Classical magnetic separators generate a magnetic force that is very high on the side of the vessel closest to the magnet but declines rapidly with distance. The magnetic force experienced by beads in the retention area is therefore greatest, while the beads farthest away experience the lowest force.
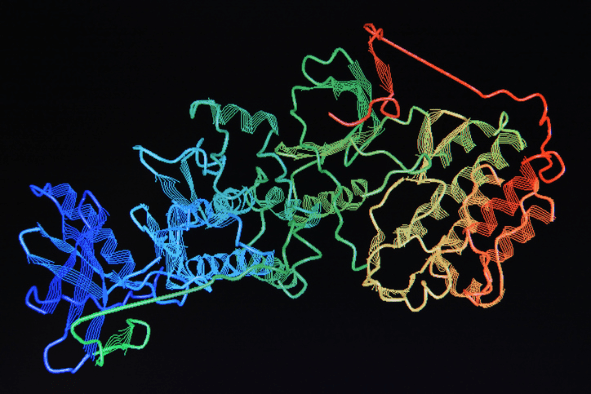
Proteins are one of the four macromolecule building blocks of life. The other three are carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Proteins are long strings of amino acids that fold together into what are called “hierarchical structures” in order to perform specialized functions within the cells and tissues of all living organisms.
Customizable Nanoframeworks are one of the most exciting innovations in the world of nanochemistry. There are two main classifications of nanoframeworks. The first is the Metal-Organic framework (MOF). A MOG is a classification of a compound that consists of a metal linked to an organic ligand to form a coordinated structure in 1, 2 or 3 dimensions.
The second is a Covalent-Organic framework (COF), which is a crystalline porous organic framework with two or three dimensional properties. A COF is usually, but not always, limited to light elements (H, B, C, N and O) . Both possess a π-conjugated system and have a wide porous volume that can be tuned with the selection of a linker. This linker also has further effects on the electronic structure of the material. Thousands upon thousands of different, unique frameworks have been identified, leading to a variety of sizes that range from the nm to mm range. However, in all cases, the porosity of the framework benefits from a high surface area to volume ratio, leading to many different applications using a delivery mechanism that benefits from rapid diffusion.

Traditionally, biomagnetic separation users have not monitored the separation process. The nature of classical separators, where the magnetic force changes with the distance, means you can determine when the separation is complete (the buffer becomes transparent), but it is difficult to interpret the optical changes during the process. This is because every location sampled will have a different bead concentration due to their different speeds. In addition, it is difficult to compare different batches as even a small difference in the vessel’s position within the separator will affect the beads’ behavior.

Isolation and detection of a target molecule in cell therapeutics from a sample with high background debris or unwanted moleculesisa challenging task. Immunomagnetic-based separation is the most feasible technique to overcome the problems that come with the separation of cells and biomolecules from a complex matrix.
A fluorescent nanoparticle is a small particle containing a fluorophore that can be used to label biological material, such as a specific cell or tissue under fluorescence imaging. There are generally two locations for the particles to probe: ones that bind to the surface and others that bind internally. A large array of different nanoparticles can be used to achieve this, including but not limited to fluorescently doped silicas and sol-gels, hydrogels, hydrophobic organic polymers, and quantum dots. There are currently three main techniques for fluorescent problem.

Long read sequencing is making chromosome-scale assemblies, including diploid genomes, possible and is therefore improving our understanding of human genetic variation. But rapid improvements in long read sequencing capacity have been limited by the extraction of high molecular weight DNA. Magnetic bead-based high molecular weight DNA extraction limits DNA fragmentation, and is also less laborious and more cost-effective than other methods.

Proteins are large, complex biomolecules that perform a vast range of vital molecular functions in living organisms. Studies of the structure and function of proteins are helping to advance understanding of biology, but before proteins can be studied, they need to be isolated (i.e., purified). The best protein purification system for your application depends on the desired throughput, scale, and downstream application.

The variation in magnetic force with distance when using classical magnetic separators is rarely problematic at small volumes. The short distance between the farthest beads and the magnet means that even with the mild magnetic forces generated by a small permanent magnet, separation time is fast and the efficiency is high.

The industrial centrifuge plays an integral role in the production of more things than one would initially expect. It is a commonly used tool in the food and agricultural sector, At pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, for environmental management, and in the chemical industry. The word industry conjures up images of combination and creation—adding materials together to produce a final product. However, the separation of materials is just as important as the combination of materials. We can't create a new product until we have pure reactants to work with. This is especially important in the pharmaceutical and biotechnological realms, where reactant purity is essential to the production of a product that is safe for human consumption. This is where the centrifuge comes in. The centrifuge is used to separate heterogeneous mixtures into components varying by density.

A constant magnetic force across the whole working volume is key to consistency in biomagnetic separation processes. This ensures that all beads in the suspension experience the same force. Classical magnetic separators can't provide these conditions because the magnetic force they generate decreases with distance.

The key parameter for the biomagnetic separation processes is the magnetic force applied over the magnetic beads' suspension. The competition of this force with the drag force generated by the buffer viscosity will translate into the speed at which the magnetic beads separate.

A cell lysis buffer is a critical first component to any isolation protocol. It is fundamental to the first step of protein or nucleic acid extraction as it aids in the chemical breakdown of cell membranes and compartments, enabling target molecules to leave the cell. There are many types of lysis buffers; most are easy to make, but most are also commercially available. They are often included in kits for immunoprecipitation, co-ip protocol, nucleic acid isolation, and others. When using a lysis buffer for protein capture the addition of protease inhibitors is generally recommended in order to protect proteins.

Biomagnetic separation has a wide range of applications in life sciences, from cell sorting to protein purification. But we regularly speak to laboratories and companies whose magnetic separation protocols lack necessary information on the key parameter: magnetic force.

By improving the capture and isolation of biomolecules in complex matrices, magnetic beads have facilitated a leap forward in life science technologies..


We are excited to announce that we will be exhibiting at the 2022 AACC Clinical Lab Expo!
Visit our booth nr. 1559 to learn more on how to attain a safe and high-performing biomagnetic separation process. Discover how you can work with our systems with volumes from milliliters up to 50 liters, assuring batch consistency thanks to a constant magnetic force and an intuitive monitoring system.

Our understanding of genetic material has substantially increased since Friederich Miescher first extracted DNA in 1869. He discovered that a material exists within cells that precipitates out of acidic solution and dissolves into alkaline solution. He called it nuclein because it seemed to be located within the nucleus. It took until 1953 for the structure of DNA to be elucidated. It was during this time that procedures to isolate DNA began to emerge. Later, during the 1960's and 70's scientists were furiously untangling the cellular environment, and the discovery of RNA with its various forms and functions further refined DNA purification procedures.

Nanobeads have applications ranging from basic science research to clinical imaging and targeted drug delivery. Nanobeads are composites of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are defined as being less than 100 nanometers in diameter, while nanobeads are usually around 50 to 200 nanometers in diameter. There are also microbeads, but these are much larger and have diameters of at least 1000 nanometers, or 1 micrometer, which is close to the size of a cell. Bacterial cell diameters range from 0.5 to 2 micrometers in diameter, and animal cells range from 10 to 30 micrometers in diameter. The size of nanobeads is very important to their function; partly because they are so much smaller than a cell, which enables them to be used for cell labeling and isolation. In the case of magnetic nanobeads, the nanometer size imparts the paramagnetic property that is so valuable for biomagnetic separation, clinical imaging (contrast enhanced magnetic resonance (MRI)), and therapeutics such as magnetic hyperthermia for targeted tumor destruction.
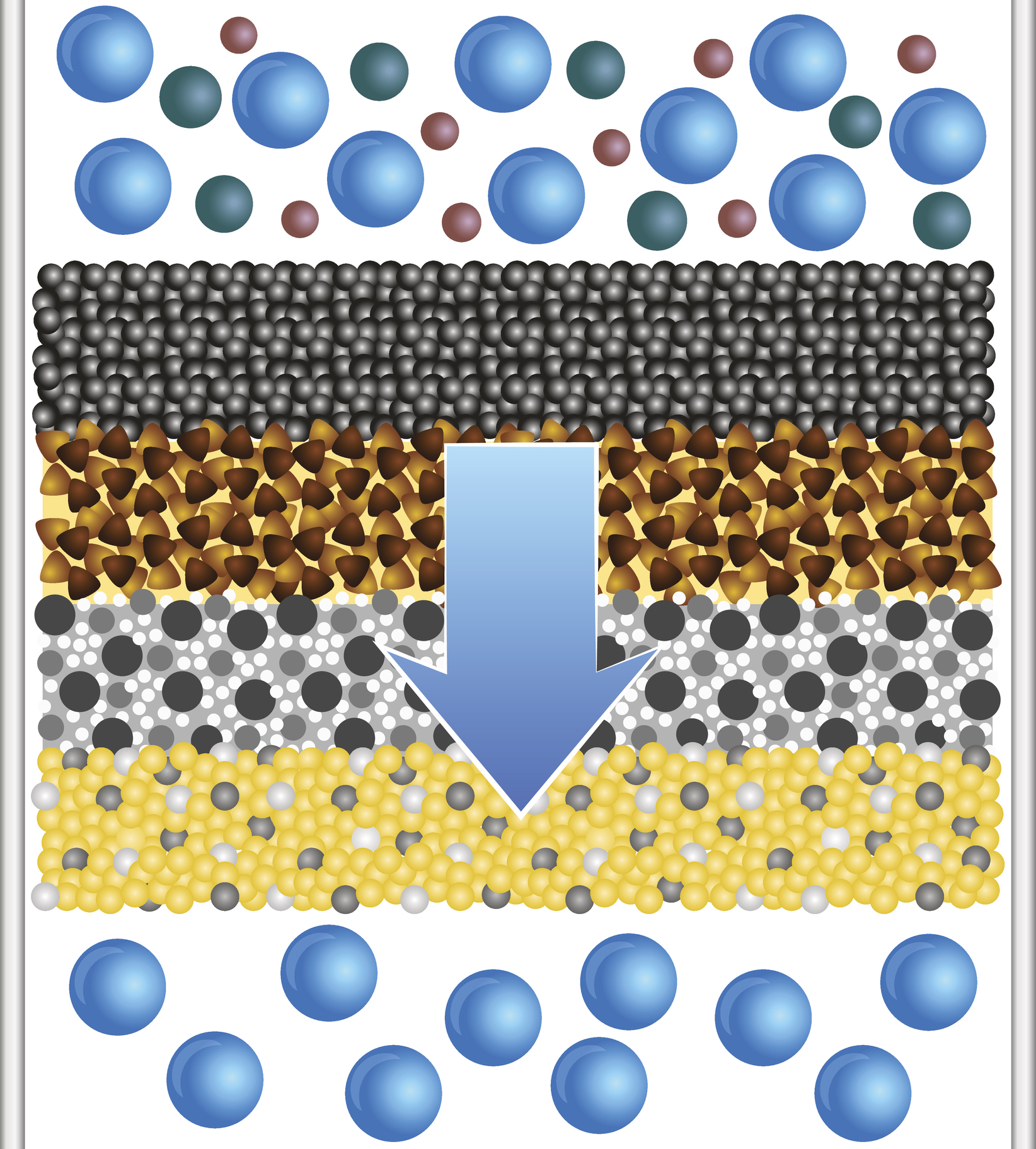
Filtration is a simple technique used to separate solid particles from suspension in a liquid solution. There are many filtration methods available, but all are based on the same general principle: a heterogenous mixture is poured over a filter membrane. The filter membrane has pores of a particular size. Particles larger than the pores will be unable to pass through the membrane, while particles smaller than the pores will pass through unhindered. Additionally, all liquids will pass through. The final result of a filtration process is a collection of residue on the filtration membrane. This residue is therefore effectively separated from the rest of the mixture that passed through the membrane.
What is upstream and downstream processing?
Introduction to upstream and downstream processing. These terms are used more in the scientific industry, for example in pharmaceutical companies. Upstream is the first half of the process and everything associated with it. Downstream is the end of the biological process. Upstream processing being the first part of the biological process, it involves the growing of bacteria in media or culturing of cell lines. Companies use bacterial or human cells to harvest products of interest. There are many products that biological companies are interested in harvesting.

Visit Sepmag at AACR (booth 1456) and Experimental Biology (booth 1530)
SEPMAG is well known for helping IVD companies to improve, validate and scale up their biomagnetic separation processes. All this know-how on the physics behind the process also benefits researchers and industries in protein purification, cell sorting, and DNA/RNA capture.

Background on Immunoprecipitation
Immuno is a prefix that means you are talking about immunity. Immunity is how the body is protected against pathogens. The immune system has a system for recognizing foreign objects, then a system for combating the presence of the foreign object. For example in humans, T-cells are a type of immune cell that recognizes antigens, structures or molecules that are foriegn. Another important immune molecule is the antibody. Antibodies are shaped like the letter Y, and the two arms of the top of the Y recognize antigens. The specific part of an antigen that is recognized is called the epitope. The antibody recognizes the epitope by its structure and sequence of amino acids. This antibody-antigen interaction serves to help the body recognize antigens. When the interaction is strong enough, it also serves as a way to neutralize antigens. Another important aspect of antibodies is that they can have highly specific interactions with an epitope, and this interaction is strong as well, also known as a high affinity interaction. These two traits, the specificity and affinity, make antibodies a great tool as well! Let’s talk more about using antibodies for a particular tool, immunoprecipitation.

Techniques and investigations that require cell isolation
Cell isolation is a technique that is done in research labs and clinical settings. Cell isolation can be done in research settings to isolate a single cell to do research on it. There is a technique called patch clamp electrophysiology which measures voltage across a cell membrane. There are several ways to do this technique, either by inserting the pipette right into the membrane, or by taking a piece of the membrane off into the pipette so that molecules are still flowing through the membrane and the pipette which is connected to a device that can measure current. Another reason to isolate cells is to use them to study the effects of a drug on cell health. One grows cells in a dish in an optimized media for growth and stability. Then a drug can be introduced into the dish and one can observe how the cell physiology changes. The molecules released from the cells can also be studied or the change in the processes or proteins in the cell can also be studied with further purification or extraction techniques.
Magnetic properties of nanoparticles are used for drug delivery, therapeutic treatment, contrast agents for MRI imaging, bioseparation, and in-vitro diagnostics. These nanometer-sized particles are superparamagnetic, a property resulting from their tiny size—only a few nanometers—a fraction of the width of a human hair (nanoparticles are approximately 1/1,000 thinner than human hair). Superparamagnetic nanoparticles are not magnetic when located in a zero magnetic field, but they quickly become magnetized when an external magnetic field is applied. When returned to a zero magnetic field they quickly revert to a non-magnetized state. Superparamagnatism is one of the most important properties of nanoparticles used for biomagnetic separation.

See you in Madrid! The Merck’s Annual 2022 Two-Day IVD Conference is back (and live), and we will be there...
After its virtual edition in 2021, Merck’s IVD conference will return face-to-face again on March 24-25, in Madrid, Spain. During these two days, international experts and scientists will address key aspects of critical IVD Immuno and molecular assays. Attendees will discuss current and future IVD technologies and market trends while taking advantage of networking opportunities and attending the supplier exhibition.
Genomic DNA extraction: an introduction
Genomic DNA is abbreviated as gDNA or called chromosomal DNA because it is packaged into chromosomes. It is the genetic code that is present in every cell and is expressed in many different combinations that lead to different cell differentiation and expression. The DNA is transcribed into RNA molecules that become proteins with many different functions. Many laboratories around the world perform genomic DNA extractions. The purpose of the genomic DNA extraction is to separate the genomic DNA from the rest of the cell contents to study it. Genomic DNA is studied by those interested in learning about specific genes and learning from genomic sequencing.
Nucleic acids refer to biomolecules composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide is the name of a nucleic acid monomer which consists of a 5-carbon sugar base bound to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. The type of nucleotide is based on the type of nitrogenous base that is bound. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) the four predominantly found bases are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine. For ribonucleic acids (RNA) the four main bases are guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil. Both DNA and RNA are part of the central dogma of molecular biology and are studied extensively. Nucleic acids are also used for research and therapeutic purposes. In order to study and use nucleic acids, it is important to have a system of nucleic acid labeling. Nucleic acid labeling can also be used to track nucleic acids.
The ability to isolate cells is important in both clinical and research settings. The goal of cell separation is to isolate one population of cells that are of interest. There are several reasons for performing cell separation, some examples are interest in studying a cell type or using it for therapy such as T-cell therapy. Some researchers are interested in cell separation to be used for creating hybridoma cell lines or for testing drugs in vitro and seeing the effect of the drugs on cells. There are many available techniques for cell separation. These techniques differ in specificity of cell selection, cost of equipment, time to complete, technology needed, and skill required. Cell separation based on cell density is rapid and inexpensive but is unspecific. Still, it is a fundamental technique that is commonly used in a variety of settings for general cell separation.
The capability of 1 μm and 2.8 μm magnetic particles to intracellularly deliver cargo proteins
In a recently published paper, researchers of the CIBER-BBN and the University Autonoma de Barcelona demonstrated that magnetic microparticles of 1 and 2.8 μm of diameter, in combination with an appropriate magnetic force, could greatly decrease the time needed to interact with and enter target cells, a clear advantage over other types of drug delivery systems.

Enzymes: an overview
Enzymes are proteins with the ability to catalyze chemical reactions. We have several articles you can read to learn more about proteins, their uses, and isolating them for research and clinical purposes. Check out our protein isolation article if you are thinking about how to best purify your protein of interest or read our protein assay article to learn more about working with proteins. Enzymes are particularly interesting and useful due to their catalytic activity. The molecule that goes into the enzyme for manipulation is called the substrate. You will often see this interaction called the “lock and key” interaction as the substrate has to fit just right into the pocket of the enzyme for it to work properly (enzymes are highly specific!), the way a key is very specific to the lock it goes into.
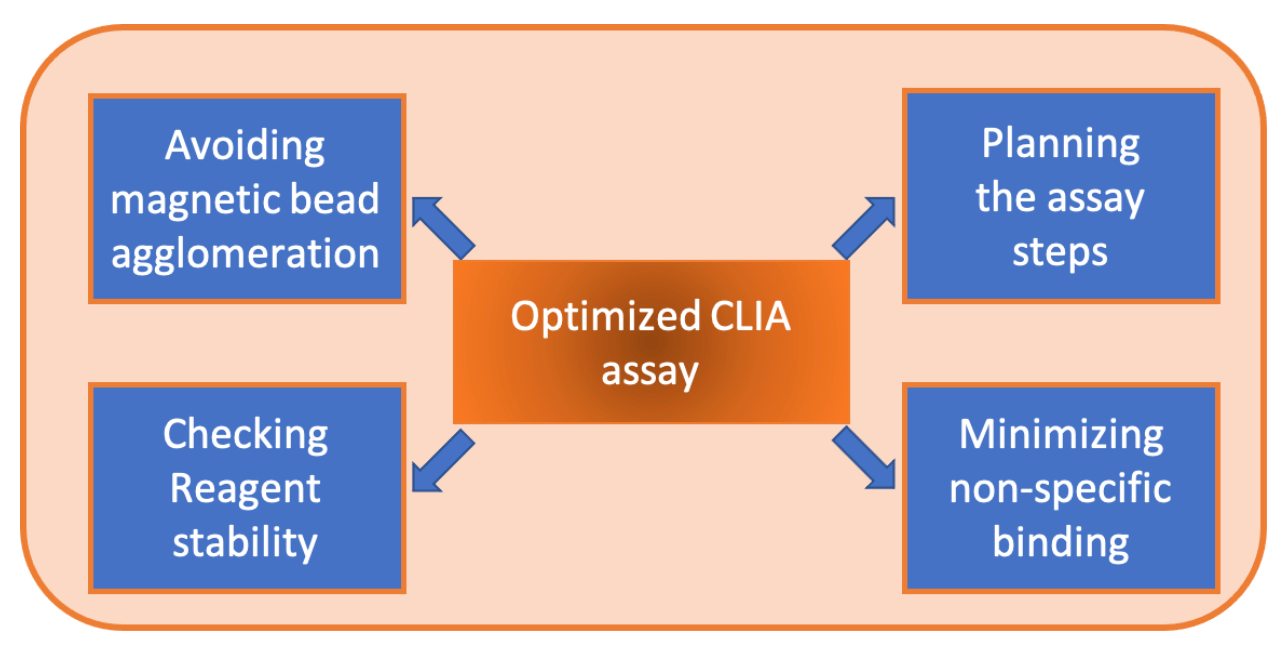
There are a few more considerations for optimizing the CLIA assay that in this chapter will be discussed. The following considerations are related to the performance of your assay.
An isolation kit helps you isolate a material of interest. When we talk about an isolation kit, we are likely talking about a kit that helps you isolate nucleic acid (RNA or DNA) or protein. These kits often contain all the buffers and hardware you need for your isolation. Let’s do a review of the types of isolation kits and how they work, then we’ll give you a general protocol to understand how the process works!
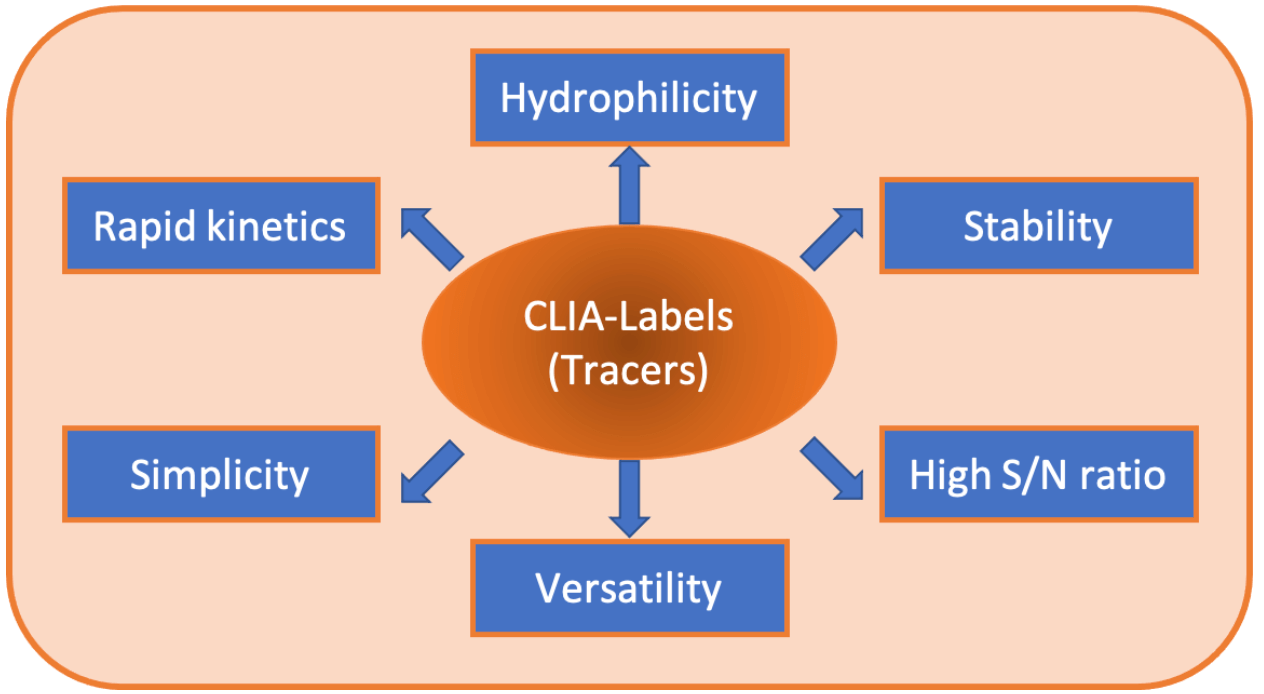
The tracer, the antigen or antibody labelled with a chemiluminescent tag for CLIA, is the next vital optimization step of a chemiluminescent immunoassay. As mentioned earlier, chemiluminescent labels generate light from a chemical reaction. Widely used CLIA labels are based on luminol derivatives or acridinium esters.

Introduction to dNTP’s
dNTP stands for deoxynulceoside triphosphate. dNTP’s are what make up one of the four macromolecules of life, nucleic acids. A nucleoside is a molecule that consists of a ribose (sugar) bound to a nitrogenous base. On dNTP’s the ribose is actually a deoxyribose because it lacks an oxygen atom on the second carbon position. There are four dominant types of nitrogenous bases that define the type of dNTP it is, they are A,T,C,G. The triphosphate is the three phosphate groups that bind the ribose as well. Our DNA is made up of these dNTPS, A binding favorably to T and C binding favorably to G. In addition to their role in the genetics of nature, dNTP’s are also used as a tool for polymerase chain reactions (PCR). Let’s discuss how PCR works and how dTNP’s are used for it.
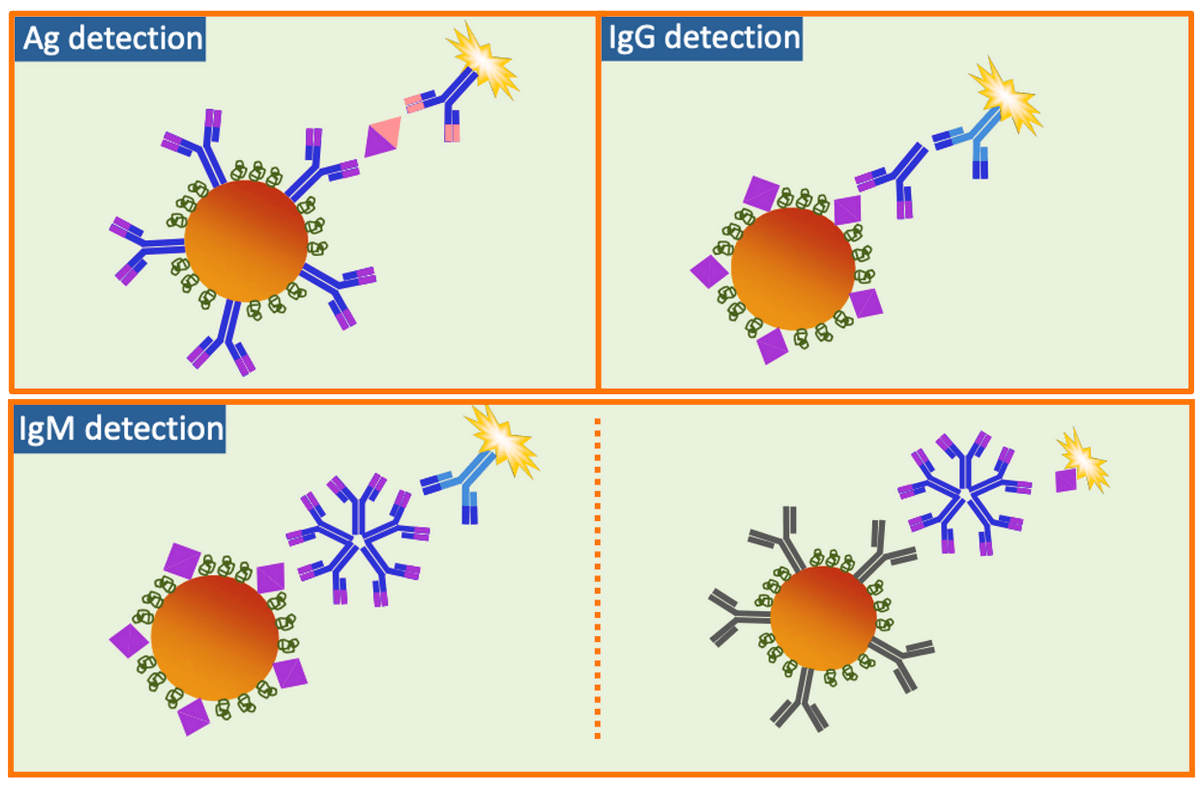
There are several types of CLIA formats that can be used depending on the target analyte of your assay. The choice of assay format will impact four major aspects of development. The first will be the choice of magnetic bead coated with antigen/s or antibody/ies for binding the target analyte. The tracer will then be required to match the target analyte using a conjugated antibody/ies or antigen/s conjugatedith a CLIA label. The assay buffer will need to be optimized to improve the specificity and sensitivity for each step. Lastly there will be components such as blockers, other linking molecules or stabilizing molecules. These aspects can be optimized once an assay format is chosen.
Overview of antibodies
Antibodies are part of the adaptive immune response of the body. After an initial defense against a pathogen from immune cells such as neutrophils, our body launches B and T cells to create antibodies to fight a pathogen. The structure of an antibody looks like the letter Y of the latin alphabet. The central part, which goes from the stalk up to the arms of the antibody, is called the “heavy chain”. A “light chain” is attached to the upper arms of the heavy chain. The stalk is also called the “Fc” region and the arms on top are called the “Fab” region. The Fab region contains the part of the antibody that binds pathogens. This region that binds pathogens is called the paratope, and it binds an epitope on a pathogen. This interaction is specific and is based on the tertiary structure and amino acid sequence. There is one epitope per paratope.

For a successful procedure for the magnetic bead conjugation, there are three important aspects to take in consideration when designing the assay: i) the planning of the conjugation protocol, ii) the density of the functional groups on the surface of the magnetic beads, and iii) the controlled magnetic separation of the beads.
When developing a CLIA it is helpful to understand what is available commercially. CLIA kits are available from many different companies that formulate reagents or components of the assay specifics for the analyte to detect and tailor made for the company analyser (platform). The solid phase can be based on superparamagnetic beads or polystyrene beads usually kept in liquid formulation. In both cases these beads require a CLIA-label reagent, discussed in more detail earlier in this ebook.

HRP stands for horseradish peroxidase, an enzyme derived from horseradish. Streptavidin is a protein derived from a species of bacteria in the genus streptomyces. Streptavidin has a high affinity for the molecule biotin. Streptavidin HRP is a streptavidin protein conjugated to HRP. HRP is used for detection/read out signals in an assay such as ELISA. Depending on which substrate you give the HRP, the enzyme will produce a different signal that you can read out with whatever hardware/technology you have in your laboratory. Let’s discuss the general protocol for using streptavidin HRP and the various substrates you can use to get an output.
Designing CLIA assays requires the consideration of different aspects, encompassing the raw materials for the reagent development & methods selection, together with the choice of the assay format. Material suppliers are a key factor for a successful design and development of an assay. An ideal supplier should be able to provide required raw materials not only at a reliable cost but also available to provide the required bulk quantities for scaling up the reagent. Moreover, suppliers should provide different lots to assess the lot to lot variability to check the impact in the assay to be developed.

Advantages of the CLIA
There are many types of assays that can be performed for detection of a molecule of interest, all with their own advantages and disadvantages. Many scientists choose to perform chemiluminescent immunoassays over the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), fluorescence or radioimmunoassays. This is because the CLIA has been shown to have an improve detection at lower concentration and a wide dynamic range.

Today we are going to talk about a piece of technology found in laboratories around the world, the spin column. It is used for “solid phase extraction.” In simple terms, the spin column has a solid material that can be used to retain or bind certain molecules while letting other molecules pass through it. When referring to spin columns, this usually refers to nucleic acid purification/isolation (DNA or RNA) or proteins. The starting material can vary from blood to tissue.
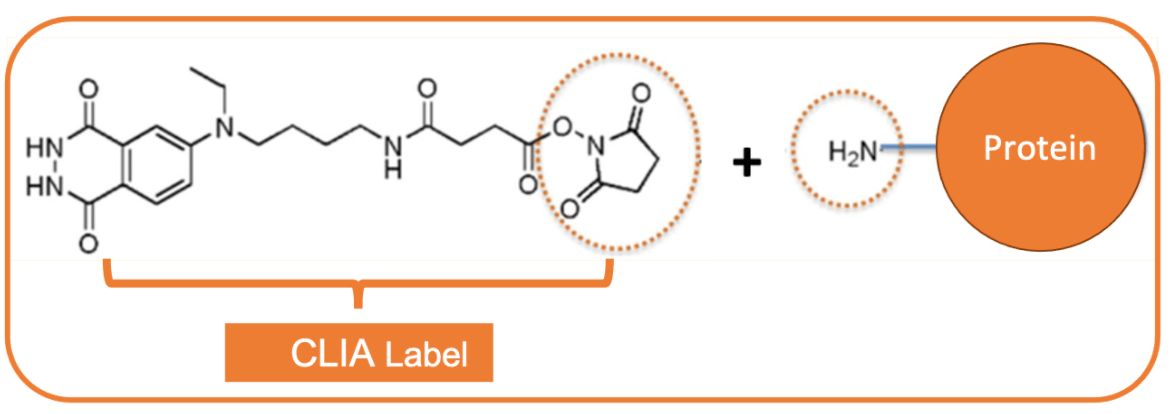
Once an optimal CLIA label (also called CLIA tag) is chosen, it must be conjugated to the protein which will bind to the analyte desired to detect. Isoluminol or Acridinium ester derivatives are often used as CLIA tags.
General introduction to RIPA
RIPA stands for Radio immunoprecipitation assay. Let’s start out by talking about what a radio immunoprecipitation assay is and why it is used. In general, an immunoprecipitation assay uses antibodies to pull a protein of interest. The “immuno” part refers to the antibody (a molecule of the immune system) and the “precipitation” refers to a substance coming out of solution. You can read about the immunoprecipitation protocol in our other article "immunoprecipitation protocol". The radio part of this refers to using isotope labeling to track molecules. In a RIPA assay you radiolabel an antigen so you can track it when it binds an antibody, while the antibody is used to precipitate the antigen.
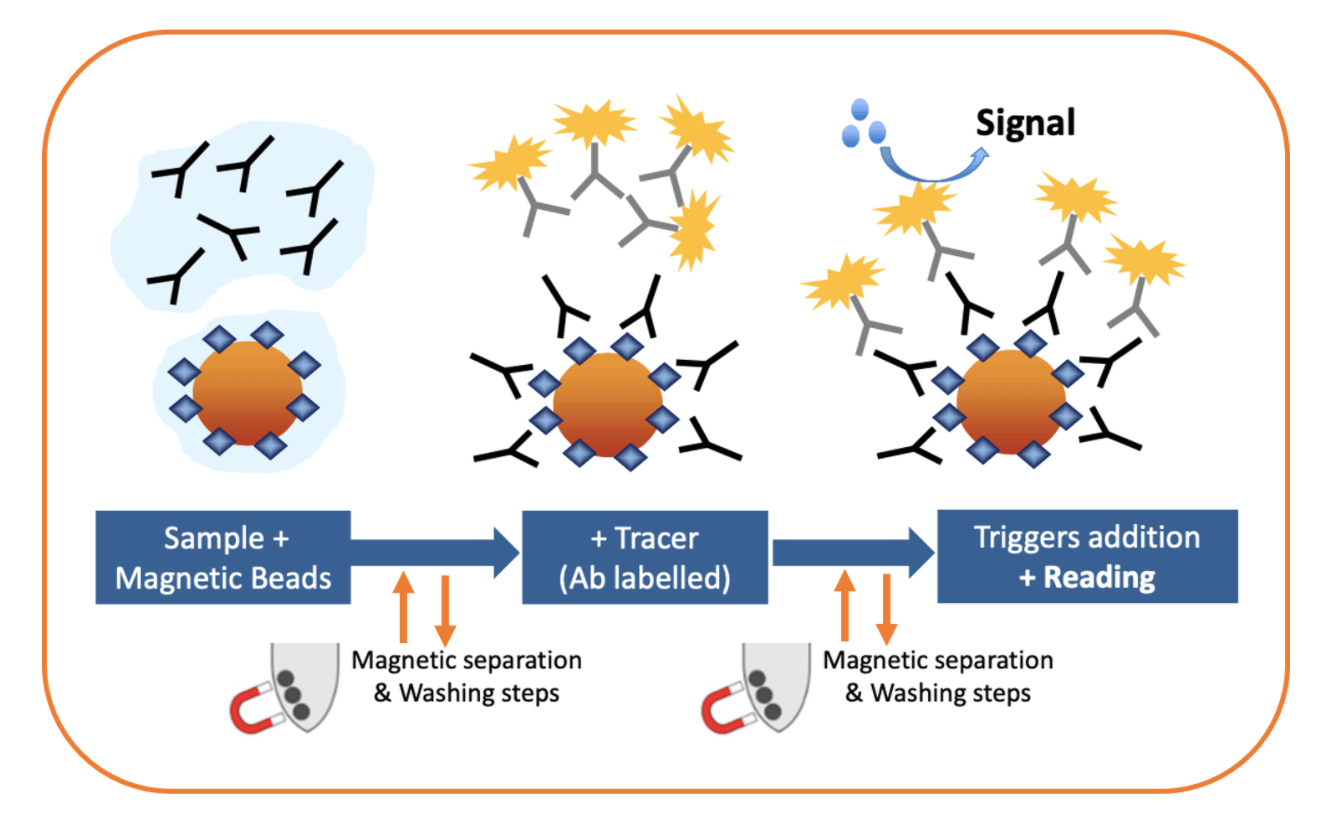
How can magnetic beads improve CLIA tests?
The combination of CLIA and magnetic beads brings together all the advantages of both parts. CLIA is known for its high sensitivity which allows the detection of analytes at very low concentrations, and thus providing an excellent limits of detection in a wide dynamic range.
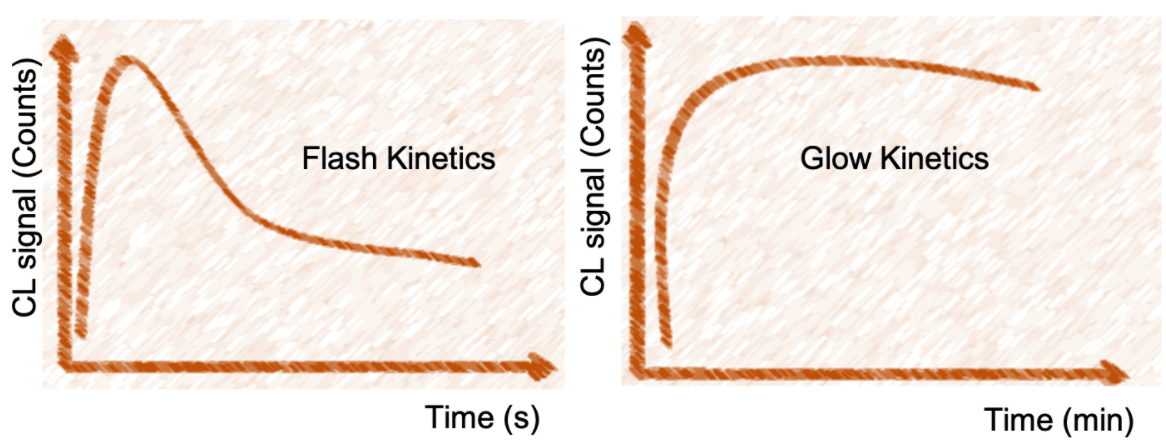
General Introduction
Luminescence is the emission of light, and it can occur in many ways. In research and biomedical industry fluorescence and chemiluminescence are often used. Fluorescence is when light is absorbed then emitted by a substance. A photon of a higher energy state is absorbed, then a lower energy photon is emitted in another range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Quick background on proteins
Proteins are a type of macromolecule made of amino acids. Each amino acid has an amino side chain, a carboxyl group side chain and between them are the atoms unique to each amino acid, typically these unique atoms are called the “side chain” or “r group.” There are 20 amino acids that make up the chains of proteins. There are a large number of combinations that can arise from 20 amino acids, their various placement in a chain, the length of the chain, and the secondary and tertiary structure of the chain. These many combinations give rise to the diversity of proteins and their functions in nature. There are two types of secondary structure that a protein chain can take, alpha helix and beta sheet. These secondary structures further take on a tertiary structure which can happen in many ways.
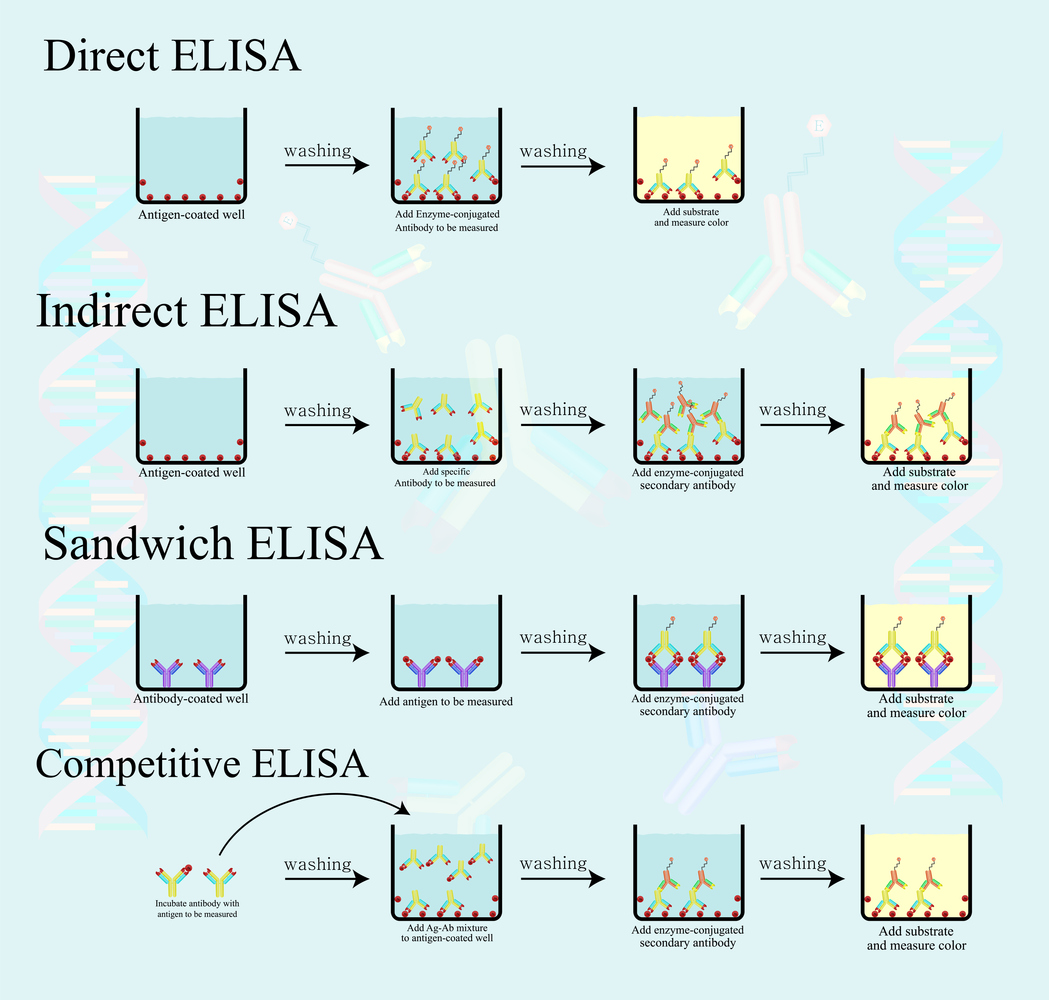
Background on ELISA
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. To help you understand the usefulness of this technique we’ll start with a brief description of how it works. The first step is to immobilize a probe molecule to your ELISA plate, these plates are usually purchased through a vendor. A probe is a molecule that binds to a target (analyte) you are hoping to capture from a sample mixture. The probe binds to the bottom of the wells through passive adsorption to the plastic. You next add your sample and allow time for your target of interest to bind to the probe in the ELISA plate wells. Lastly, a secondary antibody is added to visualize where binding has occurred through a colorimetric or fluorescent signal. There are various versions of ELISA that modify the assay for what kind of molecule you are trying to detect in a sample and whether a primary detection antibody is available for your assay for example. You can discover which ELISA is best for you in these articles about direct and indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, competitive ELISA.

This blog post is going to be devoted to acetate buffer, a widely used buffer in laboratories and scientific industries. First let’s discuss acetate, a carboxylate which is the conjugate base of acetic acid (commonly known as the main component of vinegar). Acetate has a negatively charged oxygen which is why it becomes the salt, sodium acetate. In general, buffers vary in their composition because they range in their use from helping cells grow in a petri dish to stabilizing RNA for freezer conditions. Optimization of a buffer is crucial to ensure that the correct molecules are present and the pH works for the steps of your procedure in which the buffer is used.

Introduction and inspiration of mRNA
There is a lot to learn from the mRNA (messenger RNA) that is present in cells, which makes up around 5% of the total RNA in cells. The presence of certain mRNA sequences can inform us about what proteins are most likely being translated at the moment so that biological processes can take place. mRNA has also emerged as a top vaccine for the novel coronavirus of 2019, also known as SARS-CoV-2. How can a messenger RNA be a vaccine you ask? mRNA works as a vaccine by providing our cells with the sequence to make the major protein found on SARS-CoV-2 called “spike” protein. Once our cells have made spike protein, our body will launch an immune response against it, and immune cells will make antibodies against the spike protein. To use and study mRNA, you must first perform mRNA isolation, which we will introduce in this article.
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is found in all living things. It has several functions in cells including playing a role in transcription, translation, regulation and gene expression.
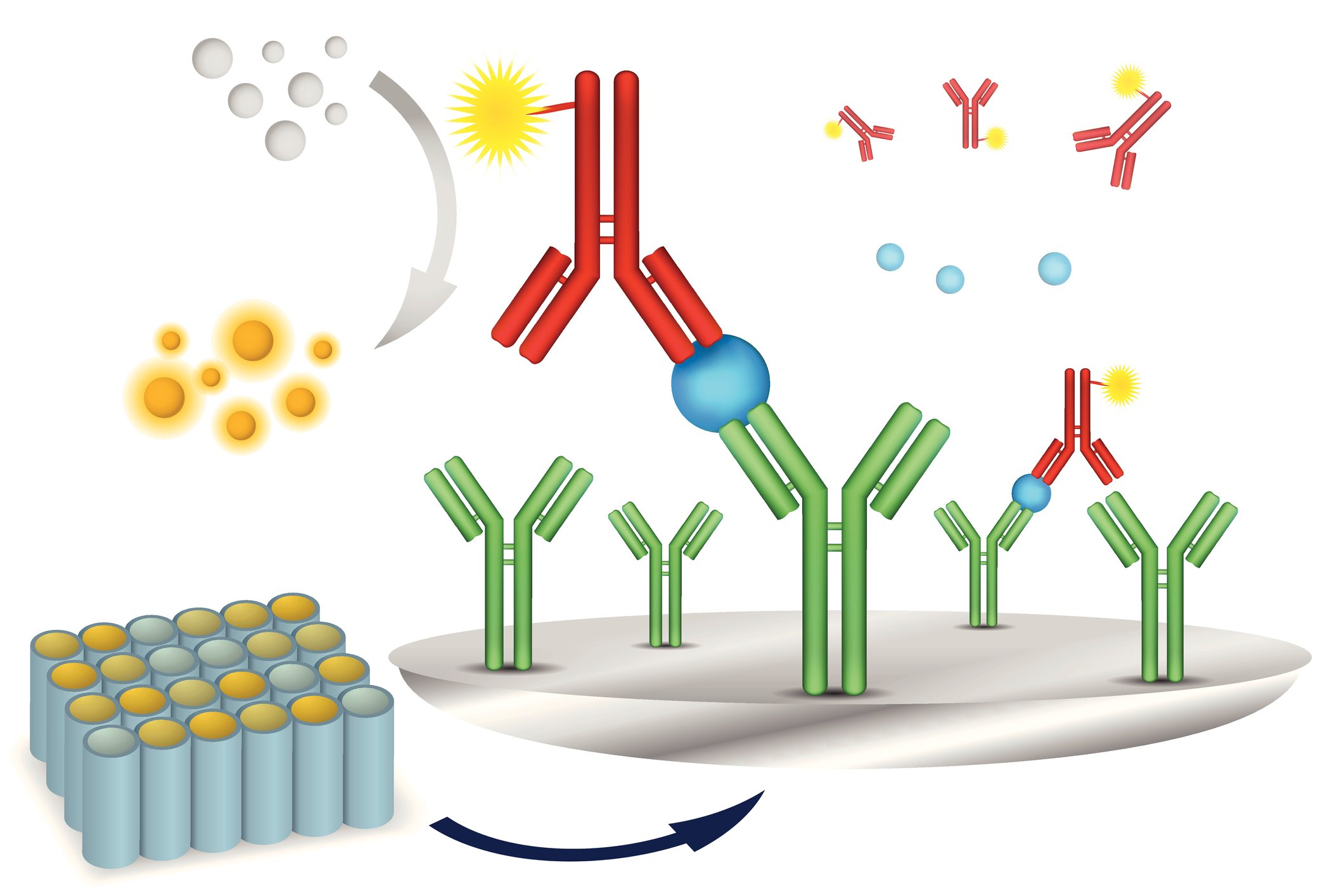
A couple of months ago we described the sandwich elisa. Here we will discuss the other two main types of elisas—indirect and direct. Elisa is an acronym for enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. The purpose of any elisa is to detect the presence of an antigen or antibody of interest. The indirect and direct elisa differ from the sandwich elisa because the antigen of interest is bound directly to the plate rather than a capture antibody. In either case, the key component is an enzyme-linked detection antibody. The enzyme is either colorimetric or chemiluminiscent. Chemiluminiscent enzymes are popular because they are easily read by a luminometer plate reader, making the process easy and highly quantitative.

Enzymes play a surprisingly important role in modern industry, and are essential to the production of more commercial products than one would initially consider. Enzymes are proteins that speed up reactions and improve yield by increasing available precursors for downstream reactions. Perhaps the most obvious use for enzymes in industryisthe production of cheese, bread, and alcohol. In these traditional applications the enzymes are part of microbial machinery such as bacteria or yeast. Over time scientists have been able to isolate specific enzymes and to understand their catalytic functions well enough to incorporate them with or without their microbial hosts into a wide variety of somewhat surprising situations. For example, enzymes are used in the production of textiles, detergents, biofuels, and pharmaceutical products. Large quantities of desired enzymes are required for these applications, and they need to be available in the purest form possible. The purity of enzymes in industry is particular important for pharmaceutical applications where the products as well as the process are susceptible to review and control by regulatory associations. Batches of enzymes in industry undergo regular process validation to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.

An elution buffer plays an essential role in every immunoprecipitation protocol or assay that requires the release of a target antigen from a capture antibody. Elution buffers are necessary in protocols utilizing a stationary affinity column, and are also required in protocols using mobile solid supports in solution.
The force of gravity will cause sedimentation of particles from a heterogeneous mixture; larger and denser particles sedimentfaster than the smaller and less dense particles. This phenomenon is useful for separating heterogeneous solutions into independent components, and for the isolation and enrichment of target molecules, cells, and cell organelles. Differential centrifugation accelerates the separation process by introducing centripetal forces many times greater than gravity. The precipitated particles form a pellet at the bottom of the tube during centrifugation. The rate of sedimentation is dependent on the size and density of the particles, so centrifugation can be used to isolate target particles simply by controlling centrifugal force or the rate of centrifugation. The rate of centrifugation is reported as angular velocity by revolutions per minute (rpm) or as acceleration(g). RPM is dependent on the radius of the rotor in the centrifuge.
Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) are cancerous cells that dissociate from a tumor and circulate throughout the bloodstream. Therefore, the detection of CTCs in the bloodstream is an indicator of cancer progression and an early sign of metastasis. CTCs are not hematopoetic in origin, and they do not express the cell surface marker CD45. However, they do express the surface antigen EpCAM, which is commonly expressed on epithelial cells. Immunomagnetic separation methods take advantage of these surface markers to isolate CTCs from centrifuged blood samples.

What is process validation and why do we do process validation?
Good manufacturing practice is an essential part of the production of human drugs, veterinary drugs, biological and biotechnology products, and pharmaceutical ingredients. These commercial processes are subject to regulatory oversight and must ensure that every aspect of the production process is carefully scrutinized. The purpose of process validation is to collect data and scientifically analyze the production process from conception to large scale production. An updated process validation protocol is essential to ensuring product quality and consistency. Many laws have been established to mandate process validation in order to protect consumers, especially in the case of pharmaceutical products.
Process validation in the pharmaceutical industry takes the same form as process validation in all other industries, but the stakes are higher because the product is made for human consumption. Moreover, pharmaceuticals are made to alter the natural biochemical pathways in the human body, so these chemicals must be formulated correctly and consistently every time. Additionally, the products must be stored properly and shipped under climate-controlled conditions in order to ensure efficacy once reaching the consumer.
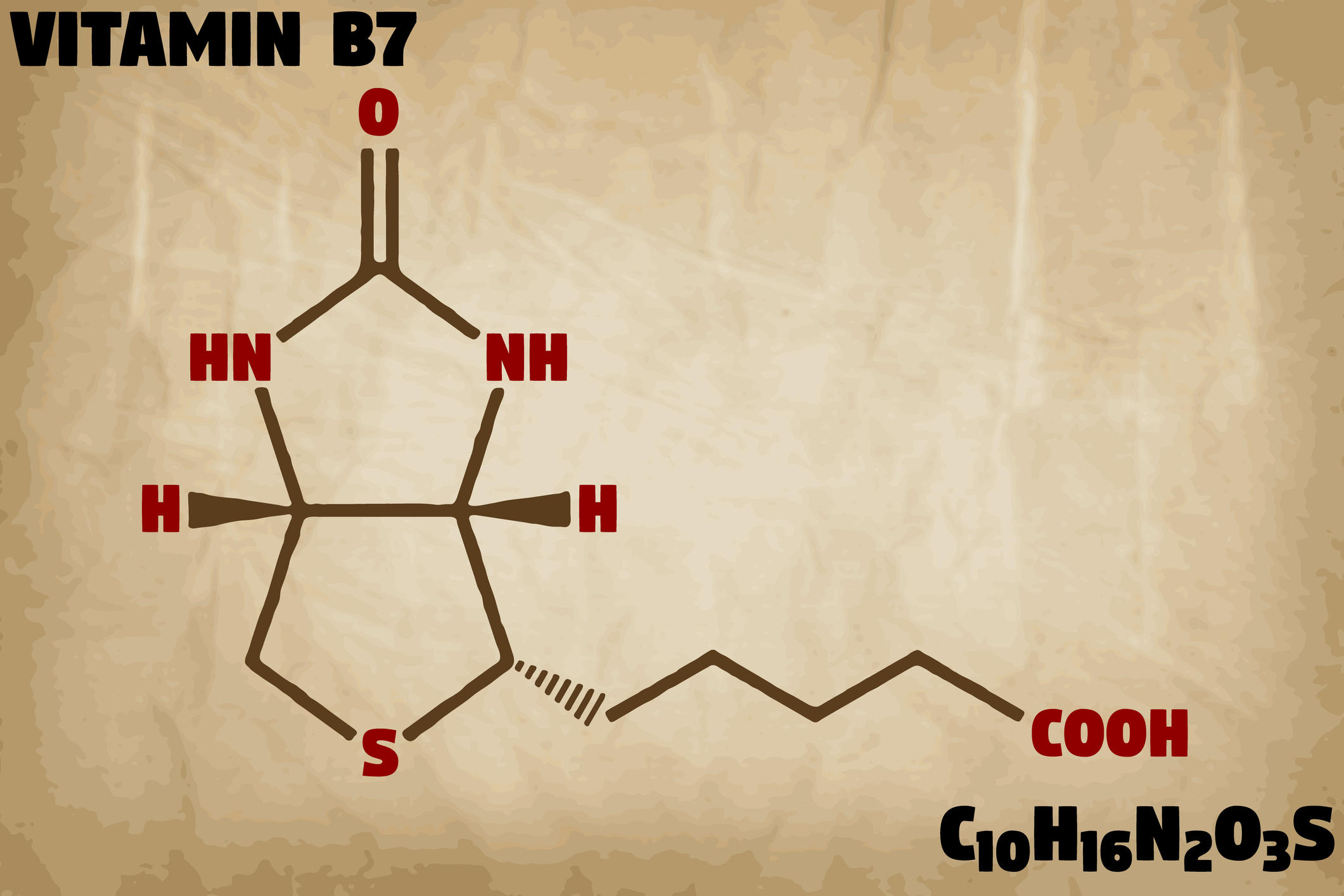
Biotinylation kit means attaching a biotin tag to a molecule. Biotin is a natural molecule that is also known as vitamin B7. It is an important component in a healthy diet, but it is also very useful in the laboratory as a method for protein conjugation. In the laboratory, he purpose of biotinylation is to create a controlled site for biotin-streptavidin affinity binding.
What is biotin labeling and how does streptavidin bind biotin?
The biotin fits exquisitely into a biotin-binding pocket in each of the four binding sites per streptavidin molecule, and it is held in place with hydrogen bonds. Additionally, once the biotin is bound, a conformational change in the streptavidin allows a small “cap” to close over the biotin in the binding pocket. As a result, biotin and streptavidin have an extraordinary affinity for each other (Kd=10^-15). With such a low dissociation constant, once the biotin and streptavidin are bound it is unlikely that they will dissociate. This affinity is resistant to changes in temperature, pH, and salt concentration and is extremely specific. It is often thought of as a nearly covalent bond. These properties make biotinylation a useful tool for engineers who are developing new purification and detection methods. A commercially available biotinylation kit makes the process even easier.
The difference between IP and coIP
Co-immunoprecipitation (coIP) is a protein extraction technique that specifically targets protein-protein interactions. It is slightly different from immunoprecipitation. Immunoprecipitation utilizes antibodies immobilized on a mobile support to capture target proteins. Co IP protocol takes this concept one step further by using antibodies to target not only the direct antigen that binds to the antibody, but also any protein that binds to the antigen and is pulled out with it. This makes co-ip protocol an ideal technique for studying protein complexes. The main concern when developing a co-ip protocol is to ensure that the lysis, wash, and elution buffers do not denature the proteins. Otherwise the tertiary structure of the proteins will deteriorate and the protein-protein interaction may be altered or completely lost.

Gold nanoparticles display unique optical properties. These properties make gold nanoparticles useful tools for biotechnology and medicine. Gold nanoparticles are also called nano gold or colloidal gold due to the fact that they are less than 100nm in size and are suspended in a liquid solution. The color of the colloidal gold is dependent upon the size and shape of the gold nanoparticles comprising it. Larger particles and aggregates of particles cause the absorbance spectrum to broaden and shift towards longer wavelengths and a red color. The metallic nature of the particles makes them very useful for imaging by electron microscopy, which was one of the first applications for them. The gold nanoparticles can be functionalized with antibodies, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. This makes them very useful for scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and confocal light microscopy as well as pathogen detection and other diagnostic assays. The ability of gold to absorb light via surface plasmon resonance (SPR) makes them useful tools for photothermal therapy in the treatment of cancer.

There are three general steps to DNA extraction
- celllysis and deactivation of DNAases
- Removal of contaminating molecules: proteins, polysaccharides, salts, other nucleic acids
- Recovery of DNA
The Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbant Assay (ELISA) is the gold standard immunoassay for clinical diagnosis of disease. The basis of any immunoassay is the specific molecular recognition between antibody and antigen. This is something that the immune system does naturally. The production of monoclonal antibodies in a laboratory has become commonplace and standardized, which makes it possible to use monoclonal antibodies in immunoassays such as an IgG ELISA. The antibodies are easy to purchase from commercial vendors, and they come with quality control reports ensuring that they will recognize the target antigen.

Molecular diagnostics entails the analysis of biomarkers to help diagnose, track the progression of, or determine risk factors and prognosis of disease. Biomarkers have been identified within the realm of genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proetomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics:

Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) are relatively new diagnostic and therapeutic tool. MIPs are highly specific three dimensional polymer imprints of molecules. The power of this tool may not be immediately obvious, but it is indeed a very useful technology. The power of MIPs lies in their specificity of binding to target molecules. Before the invention of MIPs, the only way to achieve this type of specificity was through antibody-antigen binding, surface receptor-ligand interactions, or protein affinities such as streptavidin and biotin. The problem with all of these systems is that they need to already exist. But what about a target that doesn't have a known molecule with a natural affinity? Herein enters molecularly imprinted polymers.

Faster and more efficient methods of pathogen detection are in high demand. The traditional methods involve collection of patient blood or swab samples for multi-day cultures. These methods are time-consuming and require full laboratories with skilled technicians and sterile equipment. As such, they are not ideal for low-income areas or for rapid pathogen detection. There is a need for rapid pathogen technology and point-of-care diagnostic tools. Ideally, these technologies will come with a built-in validation protocol. Magnetic nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymers are good candidates for improved pathogen detection systems. An additional benefit to using magnetic nanoparticles is that the separation process is easy to quantitatively measure with a validation protocol.
Enzymes are the catalysts for biochemical reactions. As such, they speed up the transition from reactants to products without being consumed in the process. Multiple enzymes can be found in every cell, from bacteria up through to humans. We as humans have found ways to exploit enzymes to produce food products, fuel, pharmaceutical products, biotechnological tools, sensors, and much more. The potential uses for enzymes are seemingly limitless. The creation of solid support structures with immobilized enzymes has improved our ability to reuse enzymes in a controlled manner for a variety of applications. Immobilized enzymes can be reused multiple times before their efficacy is lost. This allows them to be an affordable part of industrial processes.

Pharmaceutical validation is important to the manufacturing process to ensure product consistency and safety. It involves regulation of all raw materials and production procedures as well as testing of final product. The general rule of thumb is to follow good manufacturing practice (GMP). This demands that all protocols be up to date and followed by trained personnel. It also requires that equipment be well-maintained and inspected. In the case of clean-room usage the clean room needs to be verified.

In bacteria there are two main types of DNA—genomic and plasmid. Plasmid DNA is unique to bacteria. Eukaryotic cells don't typically have plasmid DNA unless it was put there by transfection for experimental purposes. The most important goal when isolating nucleic acids is to obtain the highest purity genetic material possible. When isolating genomic DNA it is important to remove plasmid DNA and RNA from the sample. Similarly, sometimes an experiment calls for the isolation of plasmid DNA, and the selective removal of genomic DNA is necessary. Also, some commercial RNA isolation kits include gDNA eliminator spin columns to remove genomic DNA from the isolate.
The ability to isolate and identify proteins from a biological solution is fundamental to basic research and clinical diagnosis. Proteins are the workhorses of the organism; they send and receive messages, they control the flow of information across the cell membrane, and they enact cascades of action within cells. It is rare that a single protein works alone, so it is imperative to understand how proteins interact with each other if we are to understand the nature of our bodies and to discover and treat disease.